一些背景
这几天研究了一下 html, css, js, react, vue, tailwindcss, gatsby 等等一大堆前端的东西,最后把博客基于 gatsby 用 React 重写了一遍,样式借鉴了之前用的 hugo 主题,Archive 和 Tags 页面自己设计了一下。
事情是从 3 天前开始的,给 AC 服务器加了一个 bStats 数据统计,因为想要做一个数据图就研究了一下 html 和 js ,最终用 jquery 和 highcharts 做了这样一个图出来放到了官网。
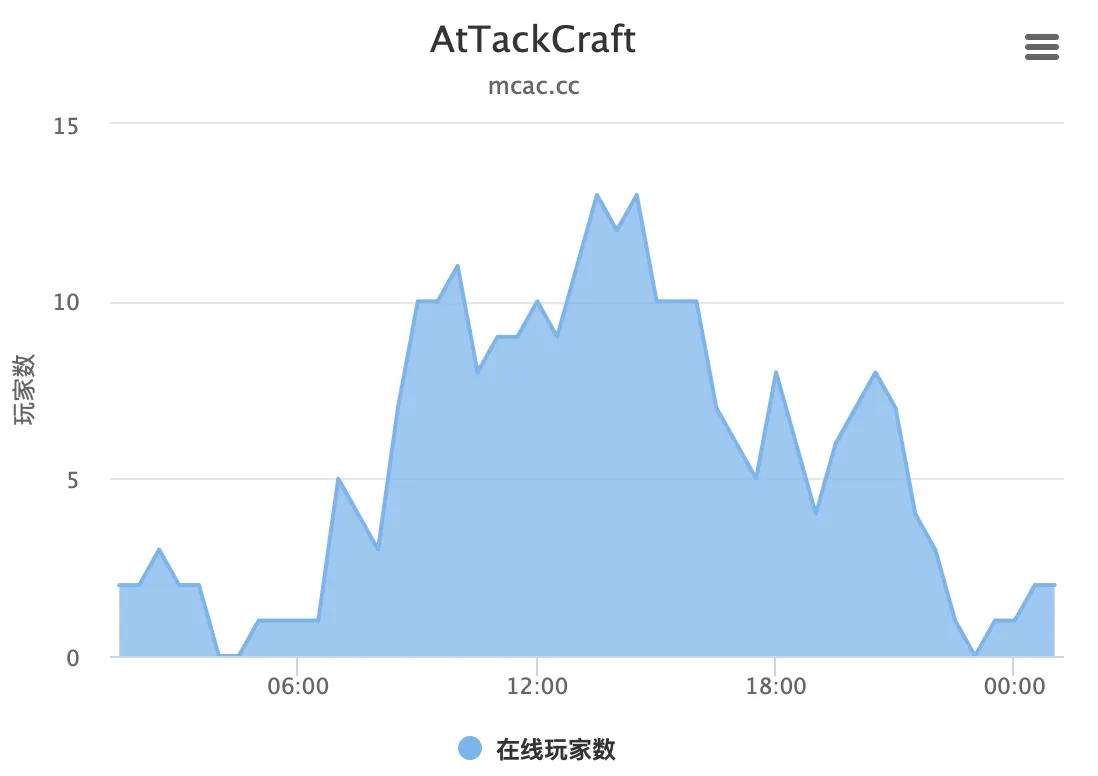
但是我又想做一个能直接返回一个 svg 文件的 api,类似于 GitHub 上的数据统计,这样可以方便的插到 html 里面,如(我放到自己 vercel 上了):
傻傻分不清楚 js 前端后端的区别,在研究这个 API 的过程中,我就不知不觉转移到了研究 AC 官网 wiki(用 vitepress 做的)如何能和官网主页用 vue 集成一下,因为此前几乎没有任何前端知识,搞不清楚一大堆的 js 框架都是干什么的,研究这个研究了很久,最后以 css 实在是太麻烦和样式相互乱覆盖告终。
之前的 vue 文件搞得我脑子疼,加之看到一个比较新且漂亮的基于 React 的深入浅出现代 Web 编程,于是开始看,另外很推荐这个教程,里面用的最新的 React 特性甚至是 2022 年新更新的。
Hello World !
const App = () => (
<div>
<p>Hello world</p>
</div>
)此时的我如下图所示:

研究了一段时间之后大概知道了 React 是干什么的,于是开始试图找个框架试一下,最后在 Next.js 和 Gatsby 中选了 Gatsby,因为据说现成的东西比较多适合个人用。
Gatsby1 重构我的博客
之前使用的 hugo-papermod 主题作者的 wiki 写的不全且 hugo 文档也不太易懂,想改点东西也改不明白,于是想着一边研究前端一边重构下博客2。
Gatsby Tutorial
Tutorial: Learn how Gatsby works
Gatsby 的文档还是写的非常清楚的,基本上跟着走一遍就明白原理了,不过 Gatsby 有个对我来说比较特殊的坑点就是用到了GraphQL,写起来稍有麻烦,好在他自带的 GraphiQL 基本上点点鼠标能把 QL 写好,加上网上查查就明白了。
Gatsby 比起直接用 hugo 这种博客生成器来说要自己做一些事情:
- 写样式
- 写页面生成器
- 渲染 markdown
- 写标签系统
以最后完毕的视角来看,不愿意折腾还是直接 hugo 方便的多,hugo 不到一秒就 build 完毕我用 Gatsby 要 build 40 多秒,而且 hugo 只是一个简单的二进制文件,维护起来可以说非常简单,但是用 Gatsby 要装海量的依赖,我最后完工的 node_modules 有近 500mb 的大小,并且有很多的依赖警告,加上 npm 很慢,配置起来体量真的是太大了。
不过 Gatsby 的扩展性就远远高于 hugo 了,还有一点我觉得比较 6,他可以整合各种内容平台包括 Wordpress 上的内容,我也是这才知道还有 CMS:内容管理系统这样的东西存在。
Conveniently, Gatsby has a powerful feature called the data layer that you can use to pull data into your site from anywhere. Want to keep your blog posts in WordPress, your store products in Shopify, and your user data in Airtable? No problem! With Gatsby’s data layer, you can combine data from multiple sources, which lets you choose the best platform for each type of data.
要做的事情
做的过程中仓库的一个 todo list track
- Based on Gatsby Blog Starter
- set up tailwindcss
- 基于 hugo-papermod 设计完成主页
- 卡片式文章列表
- Header & Footer
- 加入 frontmatter cover
- markup 排版使用 tailwindcss typography
- 增加 Tags 标签功能
- 修改 Tags 页样式
- 增加 Archive 页
- 增加卡片点击悬浮效果
- 增加 Table of contents
- 增加深色模式
- slug 格式
-
分页首页直接跳转 Archive - 草稿 frontmatter draft
基本逻辑
单个页面直接用 React 生成,博客页面用 Graphql 查询数据后创建 post 页面,post 页面内再用 Graphql 获取 post 的frontmatter tableOfContents html数据。
样式 & 适应手机
之前甚至我不知道有 css 库这种东西,还以为组件现成的只能用 ant design 这一类东西,但是这些东西又和我的需求不搭边,光是研究怎么用 css 把字放在图片上面就研究了很久,结论是狗都不做前端。最后发现 tailwindcss3 这个好东西,简单写几个字就做出来好的 UI 了,当然目前我的状态是没有尝试 tailwindcss 以外的 css 框架。基于 Gatsby 的具体操作文档Get started with Tailwind CSS也写得很清楚了。在调了一段时间之后我发现还有基于 tailwindcss 的 UI 库,可以更容易…daisyUI 感觉前端这块存在太多的东西但是新手很难找到一个大方向。

一旦开始弄点自己的有成就感的东西,还是很上头的,每天调调样式,几个小时就过去了。
使用 tailwindcss 的响应式功能,在sm情况下调整 grid 为一行,设置宽度比例更大等适配小屏幕情况。
markdown 页面生成&渲染
这里直接使用了 @tailwindcss/typography
在 post 页面模板中进行渲染。
<section
className="
prose md:prose-lg lg:prose-xl
prose-a:text-blue-500
prose-a:hover:text-blue-400 prose-img:rounded-xl
"
dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: post.html }}
itemProp="articleBody"
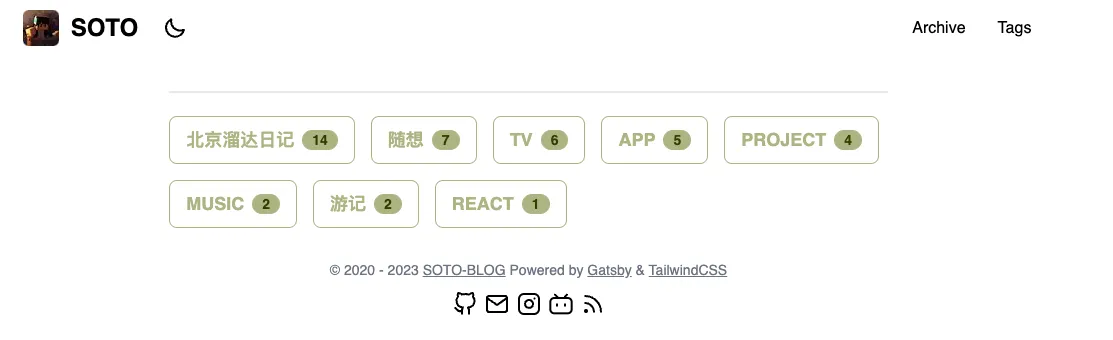
/>Tags 功能
创建每一个 tags 的页面
const nodes = tagPostResult.data.allMarkdownRemark.nodes
const tagSet = new Set()
nodes.forEach((node) => {
if (node.frontmatter.tags !== null) {
node.frontmatter.tags.forEach((tag) => tagSet.add(tag))
}
})
tagSet.forEach((tag) =>
createPage({
path: 'tags/' + tag,
component: tagPosts,
context: {
targetTag: tag,
},
})
)tags 页面模板的 Query,(draft 的 filter 用于过滤草稿)
query BlogPostByTag($targetTag: String!) {
allMarkdownRemark(
filter: { frontmatter: { tags: { eq: $targetTag }, draft: { ne: true } } }
sort: { frontmatter: { date: DESC } }
) {
nodes {
excerpt(truncate: true)
fields {
slug
}
frontmatter {
date(formatString: "YYYY-MM-DD")
title
tags
slug
tags
}
}
}
}
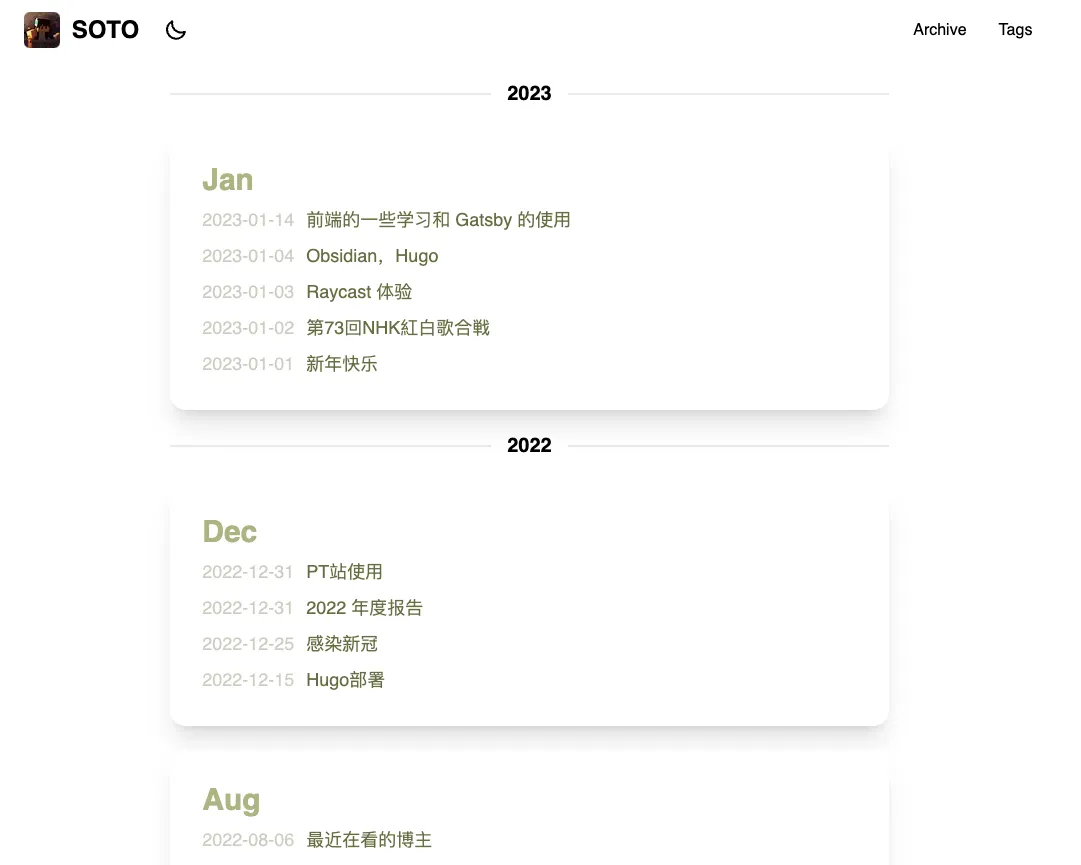
Archive 页面
按时间建 map
const timeMap = new Map()
for (const post of posts) {
if (post.frontmatter.date !== null) {
const year = new Date(post.frontmatter.date).getFullYear()
const month = new Date(post.frontmatter.date).toDateString().split(' ')[1]
if (!timeMap.has(year)) {
timeMap.set(year, new Map())
}
if (!timeMap.get(year).has(month)) {
timeMap.get(year).set(month, [])
}
timeMap.get(year).get(month).push(post)
}
}按照年-月生成卡片 (注意此处我没有设置 map 的 key,在最新代码中已经重新设置)
{
Array.from(timeMap.keys()).map((year) => {
return (
<div className="flex w-full flex-col border-opacity-50">
<div className="divider text-xl font-bold">{year}</div>
{Array.from(timeMap.get(year).keys()).map((month) => (
<div className="card bg-base-100 my-3 shadow-xl">
<div className="card-body">
<span className={'text-primary text-3xl font-bold'}>{month}</span>
{timeMap
.get(year)
.get(month)
.map((post) => {
return (
<Link
className={'text-lg hover:text-xl'}
to={post.frontmatter.slug ? '/' + post.frontmatter.slug : post.fields.slug}
>
<span className={'text-primary-content/25 mr-3'}>
{post.frontmatter.date}
</span>
<span className={'text-primary-content/75'}>{post.frontmatter.title}</span>
</Link>
)
})}
</div>
</div>
))}
</div>
)
})
}
自定义 slug
创建页面时规定路径。
posts.forEach((post) => {
createPage({
path: post.frontmatter.slug ? post.frontmatter.slug : post.fields.slug,
component: blogPost,
context: {
id: post.id,
},
})
})Link 时指向
<Link to={post.frontmatter.slug ? "/" + post.frontmatter.slug : post.fields.slug} itemProp="url">深色模式
在 daisyUI 配置好主题颜色,再设置切换按钮。
<input
type="checkbox"
onChange={(e) =>
e.target.checked
? document.documentElement.setAttribute('data-theme', 'soto_theme_dark')
: document.documentElement.setAttribute('data-theme', 'soto_theme')
}
/>链接问题
之前在 hugo 上麻烦的内部链接在 Gatsby 上也意外的简单,直接用 markdown 的链接格式不要带 md 后缀就能够实现在 Obsidian 和 Gatsby 上都生效
官方有一个内部链接截断插件gatsby-plugin-catch-links,但我没看明白他做了什么,在存在自定义 slug 的情况下,内部链接转换也会很麻烦,或许需要自己写一个转换的插件,放弃这个了。还是采用之前的 obsidian 双括号加一个 slug [[...]](/slug)
另外,页面上使用 Gatsby 自带的 Link 组件有预渲染的作用
The Gatsby
Linkcomponent provides a performance feature called preloading. This means that the resources for the linked page are requested when the link scrolls into view or when the mouse hovers on it. That way, when the user actually clicks on the link, the new page can load super quickly.
RSS feed
使用gatsby-plugin-feed插件,按文档进行基本配置。这里有一个坑,gatsby develop状态下不会更新rss.xml的内容,需要gatsby build之后才会更新。
{
resolve: `gatsby-plugin-feed`,
options: {
query: `
...
`,
feeds: [
{
serialize: ({ query: { site, allMarkdownRemark } }) => {
return allMarkdownRemark.nodes.map(node => {
return Object.assign({}, node.frontmatter, {
description: node.excerpt,
date: node.frontmatter.date,
url: site.siteMetadata.siteUrl + (node.frontmatter.slug ? (`/` + node.frontmatter.slug) : node.fields.slug),
guid: site.siteMetadata.siteUrl + (node.frontmatter.slug ? (`/` + node.frontmatter.slug) : node.fields.slug),
custom_elements: [{ "content:encoded": node.html }]
});
});
},
query: `{
...
}`,
output: "/rss.xml",
title: "SOTO-BLOG"
}
]
}SEO
配置 opengraph 和 twitter card
return (
<>
<title>{defaultTitle ? `${title} | ${defaultTitle}` : title}</title>
<meta name="description" content={metaDescription} />
<meta property="og:title" content={title} />
<meta property="og:description" content={metaDescription} />
<meta property="og:type" content="website" />
<meta property="og:image" content={metaImage} />
<meta name="twitter:card" content="summary_large_image" />
<meta name="twitter:creator" content={site.siteMetadata?.social?.twitter || ``} />
<meta name="twitter:title" content={title} />
<meta name="twitter:description" content={metaDescription} />
<meta name="twitter:image" content={metaImage} />
{children}
</>
)效果:
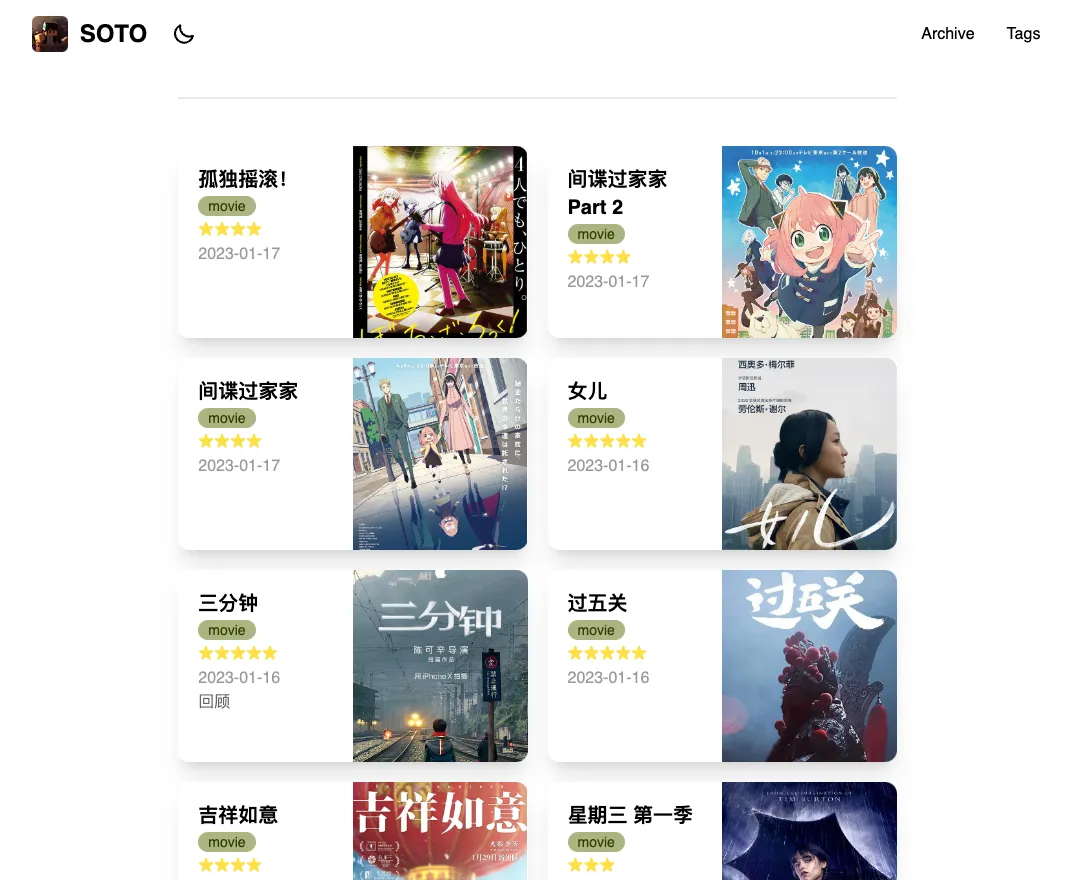
集成豆瓣数据的尝试
首先用 Chrome 插件豆伴导出豆瓣数据为 JSON,(直接备份数据库可以拿到 json 数据)
Gatsby 读取 JSON 方法 Sourcing Content from JSON or YAML
倒置,截取前一百
const nodes = JSONData.interest.reverse().slice(0, 99)提取数据
const type = node.type
const title = node.interest.subject.title
const stars = node.interest.rating ? '★'.repeat(node.interest.rating.value) : null
const date = node.interest.create_time.split(' ')[0]
const cover = node.interest.subject.cover_url
const url = node.interest.sharing_url呈现到页面上
Footnotes
-
Gatsby: https://www.gatsbyjs.com ↩
-
tailwindcss: https://tailwindcss.com/ ↩
